Banana Production in Africa
Page Content

Bananas and plantains are the world’s fourth most important food crop and are of critical importance to the food
security and income generation of more than 70 million Africans. There
are various types of banana unique to Africa, and these can be eaten
fresh, cooked,
fried and processed to be served as baby food, juice and beer. East
African Highland cooking banana (EAHB) and plantain makes up
approximately 70% of all bananas grown on the continent. People living
in the highlands of central Africa eat more bananas than anyone else in
the world, deriving 35% of their daily calories from the crop. In the
lowland of the Congo basin, farmers grow a greater diversity of
plantains than anywhere in the world. Moreover, these perennial plants
are the backbone of many farming systems as they produce fruits the year
round, protect the soil from erosion, and survive floods, drought and
civil conflict. Sweet dessert bananas are grown everywhere and are
consumed as a snack, but they form a smaller portion of the total
African crop. The Cavendish banana, which dominates export markets
worldwide, is now being planted in increasing quantities on large
commercial farms in western, eastern and southern Africa. |  |
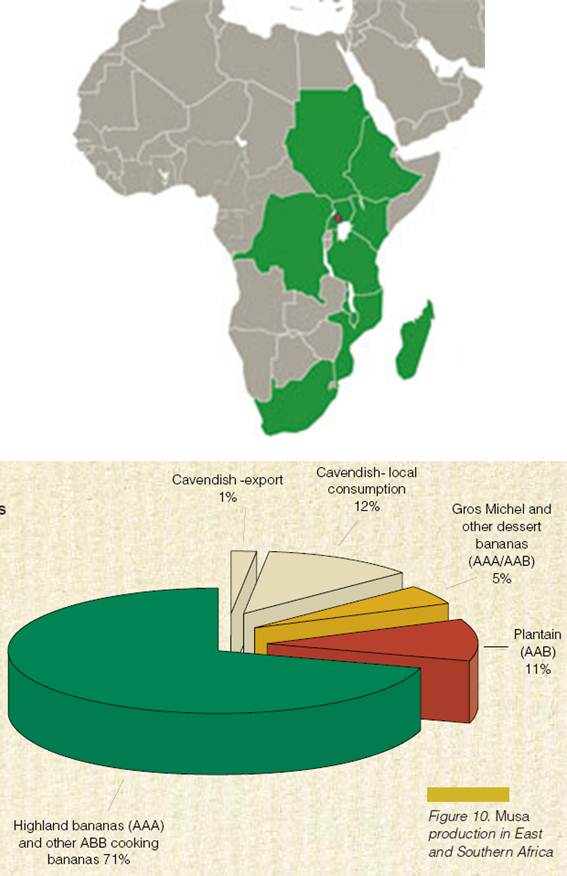
Musa production in East and Southern Africa(Source: Bioversity International)
| 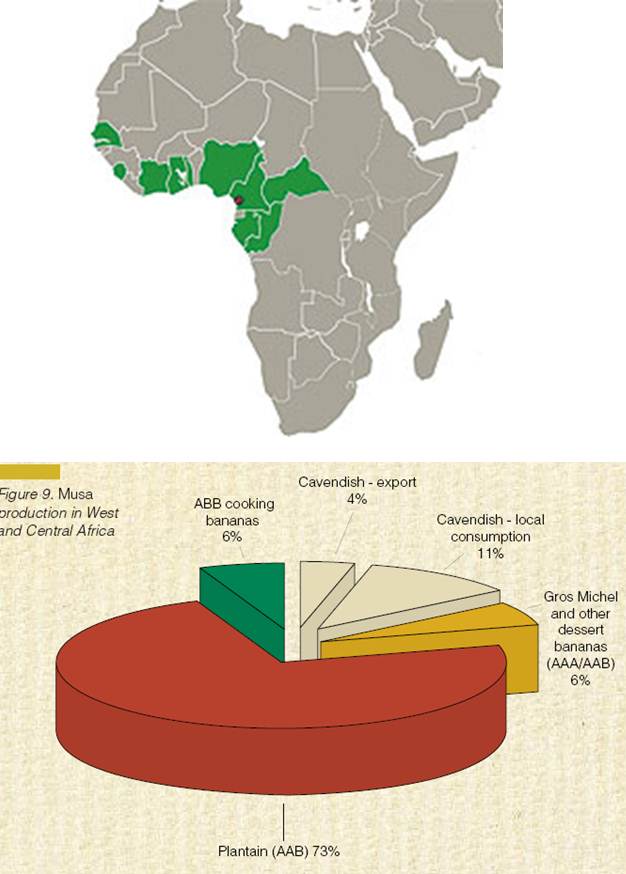
Musa production in West and Central Africa(Source: Bioversity International)
|

