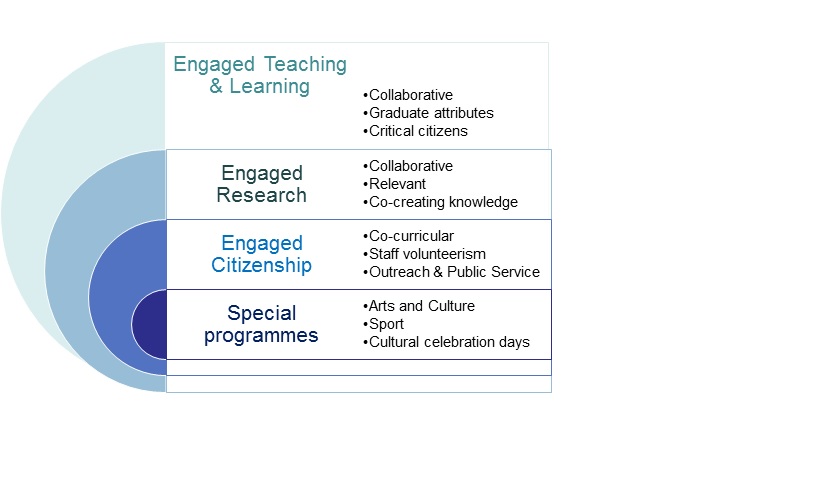
Engaged learning and teaching refers to a form of teaching and learning which may take a curricular or co-curricular character, is assessable for academic credit and includes structured reflection by learners and educators. It is embedded in reciprocal benefit for all involved and encompasses all pedagogical practices that favour experiential type learning where knowledge is socially constructed and activity based. It aims to facilitate student transition from university to workplace, is associated with collaborative teaching practice where professionals in practice become mentors and co-educators of students and provides opportunities for collaborative research that focus on teaching practice. Students are mentored to be a new generation of engaged critical citizens and social change enablers.
Engaged research is research employing inclusive participatory and collaborative methodologies, such as participatory action research; as well as research addressing prominent themes of the Sustainable Development Goals and the National Development Plan, such as social cohesion and nation building, human development, poverty and inequality, transformation, social justice, state capability, educational outcomes, jobs and livelihoods, innovation, sport and healthy lifestyles, health care and sustainability. Engaged research promotes science with society rather than science for society. SU acknowledges that generating knowledge for the sake of knowledge itself is important and may have indirect SI, but SI through research is best achieved through engaged research.
Engaged citizenship, e.g. student volunteerism as a structured, co-curricular learning experience; staff and alumni volunteerism as instances of responsible active citizenship; and public service rendered by SU staff based on their fields of expertise increasing the capacity of societal organisations and institutions.
Various SI special programmes in faculties and in the broader university advance the SI of the University. In addition to faculty initiatives examples of university-wide initiatives are Maties Sport, INNOVUS, the museum and Woordfees with its accompanying entities, namely Woorde Open Werelde, the BUYA Project and the university choir.
Societal interaction and the building and servicing of partnerships with external social partners with whom SU interacts in a mutually beneficial way, is a cross-cutting component of SI. Societal interaction is an imperative for engaged scholarship. Through partnerships access to university facilities and development opportunities are new offerings. The university engages in bottom-up civil society based projects that build agency and solidarity in social groupings in its close proximity. It enacts change by focusing on building social capital which will enable these groups to take responsibility for their own development. The university partners with government and business through innovative practice knowledge that supports economic development and infrastructure development in sustainable ways.

